

Application Notes-900
Power Supply Functional Testing
A DC power supply is a
device which transfers AC main power to a required DC output V/A/W rating. A
good power supply should be reliable, meet all required functional
specifications, full protection features, safety and Electromagnetic
compatibility requirements. This application note is focusing on the testing
of functional specifications and protection features.
Power supply testing methods for design, production, and quality
verification require sophisticated electronic equipment. Different power
supply configurations and output combinations also dictate the need for
versatile test instruments that can accommodate a broad range of
specifications.
Prodigit 3300 series Mainframe, 3310/3320 series Electronic Load Module, and
3600A power supply testers provides programmability, friendly operation,
reliable test results, efficient testing and high testing quality at a
minimal testing cost. Those instruments have been broad used to test the
function of power supply by known manufacturer worldwide.
Following are functions
typically tested when qualifying a switching power supply.
1. Function test
Hold on adjust
Line Regulation
Load Regulation
Combined Regulation
Ripple and Noise or PARD.
Input Power and Efficiency
Dynamic load or Transient load
Power Good/Power Fail (Power Good Signal)
Set-up/Hold-up time
Protection test:
Over Voltage Protection (OVP)
Over Current Protection (OCP)
Short Circuit Protection
1.1 Hold on adjust/set
output voltage
When manufacturing switching power supplies, the first test step is to
adjust output voltage to within a specified range. This is done first to
ensure further specifications are met. Normally, the AC line voltage is set
to nominal and the Dc output current is set to a nominal or a maximum load
current in the HOLD-ON adjust procedure. The DVM measures the power supply's
output voltage, and adjusts the potentiometer until the voltage reading is
within the required limit.
1.2 Line Regulation
Line regulation is defined as a power supply's ability to provide a stable
output voltage under conditions of changing input line voltage.
To accurately measure line regulation, the following
equipment is required:
a. A variable line source capable of providing at least the minimum
to maximum input range of the power supply to be tested.
b. A true RMS voltmeter to monitor the input source voltage.
c. A precision DC voltmeter with an accuracy at least 10 times better than
the regulation of the unit under test.
d. A variable load for output.
Typically, the equipment is set up as shown below:
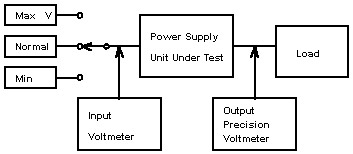 During testing, allows
the power supply unit under test to warm up and stabilize with a normal
input voltage and load, Output voltage reading should then be taken with
low, normal and high line input. Output voltage reading deviation from
normal to low and high line conditions generate the Line regulation quality
for that load condition. Line regulation is normally specified as a
percentage of deviation from nominal output at a fixed load and is
calculated using the following equation.
During testing, allows
the power supply unit under test to warm up and stabilize with a normal
input voltage and load, Output voltage reading should then be taken with
low, normal and high line input. Output voltage reading deviation from
normal to low and high line conditions generate the Line regulation quality
for that load condition. Line regulation is normally specified as a
percentage of deviation from nominal output at a fixed load and is
calculated using the following equation.![]() Line regulation can
also be specified as the absolute DC output deviation within upper and lower
voltage limit under changing input line voltage.
Line regulation can
also be specified as the absolute DC output deviation within upper and lower
voltage limit under changing input line voltage.
1.3 Load Regulation
Load regulation is a power supply's ability to provide a stable output voltage under conditions of changing load. Equipment and set-up required are very similar to that for line regulation. The only change required is the connection of an additional precision Ammeter in series to the output as illustrated below:
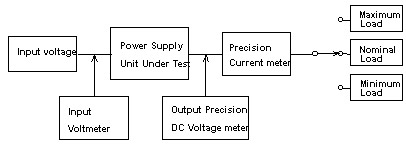
During testing, allow the power supply under test to warm up and stabilize, then measure the output voltage and use it as normal output voltage (Vnormal). Additional output voltage reading are then taken with maximum (Vmin) and minimum (Vmax) loads on the output. Output voltage deviation from normal to full load and minimum load generate the Load regulation.
Load regulation is normally specified as a percentage of deviation from nominal output at a fixed input voltage and is calculated using the following equation:
1.4 Combined Regulation
Combined regulation is a power supply's ability to provide a stable output voltage under conditions of changing line voltage and load current. It is a combination of line regulation and load regulation, and provides more exact verification of a power supply's DC output by changing line input and load output.
Combined regulation is specified as the absolute DC output deviation within upper and lower voltage limits under changing input line voltage and output load current.